How do we analyze proportions?
Binomial distribution equation
Binomial distribution: the distribution “successes” of many independent trials. There are only two possible outcomes, success and non-success.
Assumptions
- Each trial is independent of the other
- The number of “n” trials is fixed
- The probability of success, “p”, is the same for each trial
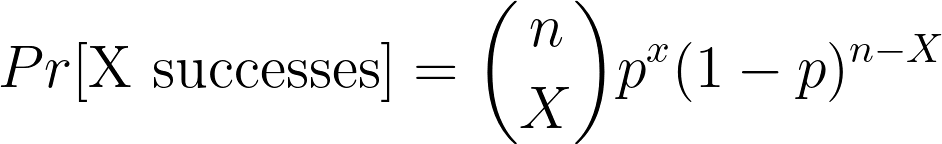
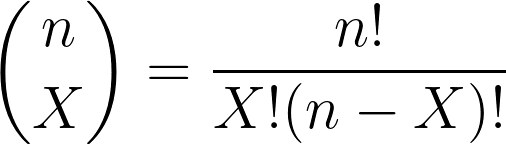
Sampling distribution of the proportion


Proportion of X successes out of n trials (p-hat).
Population standard error of p-hat.
Binomial test: used to test hypothesis that the population proportion (p) is the same as the null expectation (p0).



Estimating standard error and confidence intervals of the proportion

Approximate standard error
Agresti-Coull method calculating the CI of the proportion

